

OssiclesĮar ossicles, by definition, are three very delicate bones in the middle ear that are connected like a chain. Įar infections can occur in the tympanic cavity. This space holds the ossicles and the Eustachian Tube. The tympanic cavity is the small space in the middle ear between the tympanic membrane ear drum and the inner ear hearing organ. It can also develop otitis media, which is a category of ear inflammation.

The middle ear is most susceptible to ear infections. It also maintains air pressure balance in the skull through the regulation of the Eustachian tube. The middle ear contains most of the small organs responsible for collecting and clarifying external sound waves. If you suspect that you are experiencing hearing problems due to tympanic membrane eardrum damage, we have listed some of the best online hearing tests that you can take to self-diagnose your hearing loss. Most hearing disabilities are caused by trauma or disorders in the tympanic membrane eardrum. The eardrum collects sound waves and vibrates, passing the sound waves into the middle ear. The tympanic membrane, or eardrum is the final hearing organ in the outer ear, separating it from the middle ear. However, some believe its large blood supply can aid in keeping the ear warm. Experts have not reached a consensus on the purpose of this part of the ear.
#LABELING PARTS OF THE INNER EAR PRACTICE SKIN#
The lobule, or ear lobe, is the fleshy skin in position below the antitragus. Check out our best hearing aids review on this site. It provides a shelf-like platform at the base edge of the concha that can support the weight of medical devices. The antitragus is the cartilage that forms the bottom part of the ‘Y’ of the antihelix. It borders the concha and partially shields it from debris and particularly loud noises. This is the small, rigid part of the ears along the front of the ear, adjacent to the face. Sound waves are delivered through this canal. External Auditory Meatus The external auditory meatus, or ear canal, is a narrow canal that leads from the concha to the tympanic membrane, or eardrum. Obstruction in the concha can lead to hearing problems or conditions.
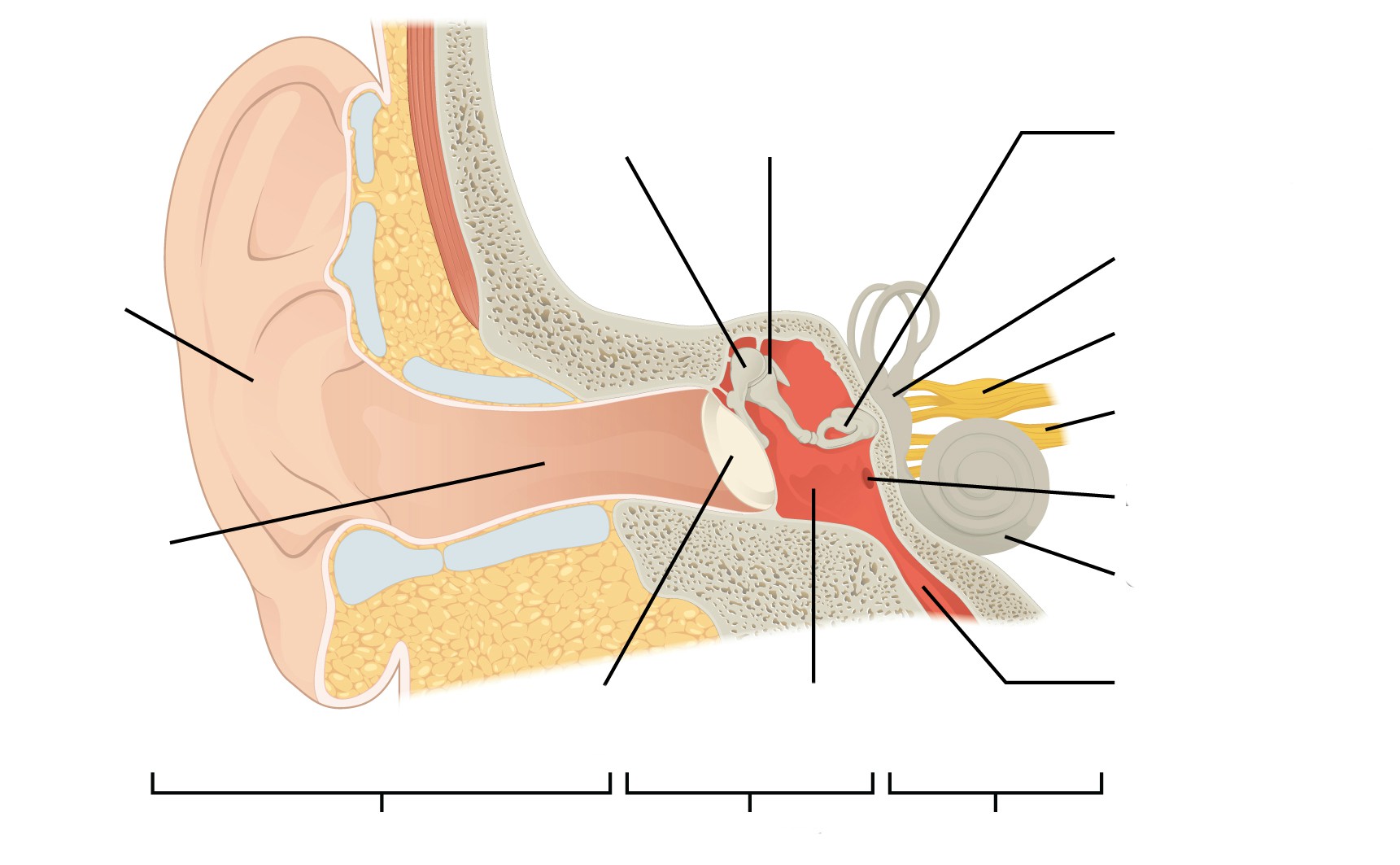
Hearing amplification devices, such as MD HearingAids or other services, are typically nestled within this cavity. It is bordered by the antihelix, the tragus, and the antitragus. The concha is the smaller cavity that funnels sound waves into the ear canal. It is more sharply defined, and it partially marks the border of the concha. The smaller, lower branch of the antihelix ‘Y’ is called the inferior crus. It is shallow and generally not well-defined. The superior crus is the larger, upper branch of the ‘Y’ part of the antihelix. It looks somewhat Y-shaped, and the two forks at the top of the ‘Y’ are called the superior crus and the inferior crus. It is more rigid and provides more strength to the outer ear. The antihelix is the smaller of the two loops. The superior crus is the larger of the two loops, and it’s the very flexible outer curve of the ear. The outer, external ear can be loosely described as two cartilaginous loops, a small one nestled inside a larger one. This sound collection is the primary purpose of all of the parts of the external ear auricle anatomy. Its dish-like shape is also essential for collecting sound waves. It is also sometimes referred to as the auricle or the pinna.Īlthough the outer ear is the least important part of the ear’s hearing function, it provides the necessary structure and protection. The outer ear auricle or external ear is composed of all of the parts of the ear outside the skull. In this section, we describe the anatomy of the ear in simple terms. Don’t worry, though-each part has a purpose that is easy to understand. The ear is an unusually complex organ in human anatomy. This article describes the anatomy of the ear in-depth and discusses ways to discover and correct potential hearing disorders. Most people also consider the ear just one part of the human body, but it’s a complex organ composed of many smaller, finely-tuned parts. Everyone knows that the ear is the organ used for hearing, but not many people are aware that it’s also necessary for balance. The human ear is the highly advanced result of millions of years of evolutionary progress.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
